+86-13928815851
+86-13928815851
Leave Your Message
-
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER



Choosing the right High Temperature Battery can be daunting. Experts, such as Dr. Emily Chen, emphasize its importance: "Selecting a High Temperature Battery is crucial for efficiency." This statement highlights the complexities involved in the decision-making process.
High Temperature Batteries are essential in extreme environments. They power systems facing intense heat. Think of industries like aerospace and geothermal energy. Here, a reliable battery ensures safety and performance. However, not all batteries are created equal. You may face challenges in determining the right fit.
Consider factors like capacity, lifecycle, and thermal stability. Misjudgments can lead to equipment failure or safety incidents. Reflect on the specific needs of your operation. A choice made without thorough evaluation could prove costly. Each application demands careful thought. Evaluating the right High Temperature Battery requires time and attention to detail.

High temperature batteries are designed to work in extreme environments. They are essential in various applications such as aerospace, deep drilling, and energy storage. These batteries can operate effectively at temperatures above 100°C, unlike standard batteries. Their unique construction allows for better performance under stress.
When choosing a high temperature battery, consider the specific requirements of your application. Think about how long you need the battery to last. Evaluate the load and discharge rates required. Environmental conditions also matter, like humidity and vibrations.
Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
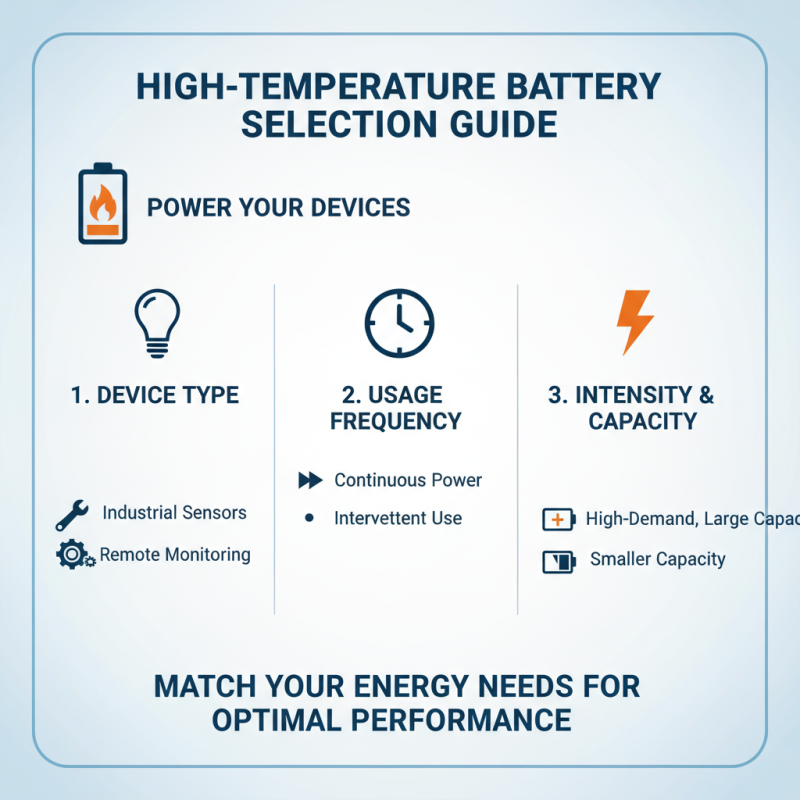
Choosing the right high temperature battery begins with understanding your energy needs. What devices will you power? How often will they be used? Think about the intensity of usage. If you require frequent and high-capacity energy, your selection might differ from casual usage scenarios.
Consider your operating environment as well. High temperature settings can lead to performance degradation. What temperature range will the battery be exposed to? Accessories such as thermal management systems might be necessary. Reflect on how the battery will be used in real-world conditions. Testing might be needed to gauge its efficiency and reliability.
Lastly, weigh the balance between cost and performance. Sometimes, a cheaper option may not meet your needs fully. This can lead to frustration and wasted expenses. Don’t rush your decision; take the time to evaluate. Understanding your requirements deeply can prevent future regrets and ensure you choose a battery that truly fits.
When selecting a high-temperature battery, understanding the available types is crucial. Lithium-ion batteries stand out for their energy density. They perform well in extreme heat, but they can be costly. Another option is nickel-metal hydride batteries. They are less expensive and can withstand high temperatures but might have a shorter lifespan. Finally, lead-acid batteries are commonly used. While affordable, they tend to degrade faster in high heat environments.
Each type of battery has its pros and cons. For instance, while lithium-ion offers high performance, it may require careful management to prevent overheating. Nickel-metal hydride batteries might be more resilient, but their capacity could diminish with frequent high-temperature exposure. The decision ultimately hinges on specific needs. Consider factors like power output, environmental conditions, and budget when navigating these choices.
Choosing the right high-temperature battery is not always straightforward. Each application demands different characteristics. Some users find it challenging to balance cost and efficiency. Detailed evaluations and comparisons are necessary to attain the optimal solution. Reflecting on user experiences can also provide insight into long-term reliability and performance.
| Battery Type | Operating Temperature Range (°C) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (Cycles) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | -20 to 60 | 150 | 500-1500 | Electric vehicles, consumer electronics |
| Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) | -20 to 70 | 45 | 1000-1500 | Emergency lighting, power tools |
| Sodium-sulfur | 300 to 350 | 150 | 2000 | Grid energy storage, renewable integration |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | -20 to 60 | 90 | 2000-7000 | Electric vehicles, solar energy storage |
| Lead Acid | -20 to 50 | 30 | 500-800 | Backup power, UPS systems |
When selecting a high-temperature battery, understanding performance metrics is crucial. Capacity, life cycle, and safety are key factors in making the right choice. Capacity indicates how much energy a battery can store. For applications in extreme environments, a higher capacity can be a game-changer. But be cautious; higher capacity may also lead to increased risks.
Life cycle is the next important metric. It refers to how many charge and discharge cycles a battery can withstand before performance drops. A longer life cycle equals less frequent replacements. However, remember that claims can be misleading. Real-world usage may differ from manufacturer promises. Always assess actual user experiences.
Safety cannot be overstated. High temperatures can compromise battery integrity. Consider batteries with advanced safety features. Look for protection against overheating and short circuits. These features may increase costs but are worth the investment.
Here are a few tips:
- Always read user reviews.
- Ask for specifications.
- Don’t skip safety ratings.
Making informed choices leads to better outcomes. Doing thorough research is essential, and keep questioning what you find.
Choosing the right high temperature battery is not a straightforward task. When assessing cost versus benefits, several factors come into play. High temperature batteries can perform at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for industrial applications. However, their price can significantly differ based on technology and specifications.
A recent industry report indicated that lithium-based batteries outperform older technologies in terms of efficiency and longevity. While these batteries may come at a higher price, their life cycle costs can prove lower due to reduced maintenance needs. Think about your specific application requirements. Will your operations justify the higher initial investment?
**Tips:** Always compare not just prices but also durability and performance metrics. A more expensive battery may offer better value in the long run. Additionally, analyze warranties carefully. Not all manufacturers provide the same coverage. It’s crucial to understand what is guaranteed and for how long.
Another consideration is environmental impact. While some batteries are more expensive, they might use sustainable materials. This choice can lower your carbon footprint and may benefit your corporate image. Cutting costs on batteries could lead to unforeseen expenses from replacements or environmental penalties.